Marine Conservation Zones (MCZs)
There are two main types of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) found in English waters, European Marine Sites (EMSs) and Marine Conservation Zones (MCZs). Unlike EMSs which are found across Europe, MCZs are found only in English waters as they are a national, rather than international, designation. MCZs are designated under the Marine and Coastal Access Act, 2009 and form a national network of sites that protect nationally important marine wildlife, habitats, geology, and ecological processes. They are a key tool in England’s protection of the marine environment. There are seven MCZs within the North Western IFCA district and you can find out more about each one below.
Different Tranches
There are now a total of 91 MCZs in waters around England, seven of which are found in the NWIFCA District. MCZs were established in a staged process of different tranches (known as T1, T2 and T3).
T1 – 1 MCZ (Cumbria Coast) was designated in November 2013.
T2 – 3 MCZs (Allonby Bay, West of Walney and Fylde) were designated in January 2016.
T3 – 3 MCZs (Solway Firth, Ribble, Wyre-Lune) were designated in May 2019
Marine Conservation Zones in the North West
There are seven MCZs within the North West IFCA district and you can find out more about each one below.
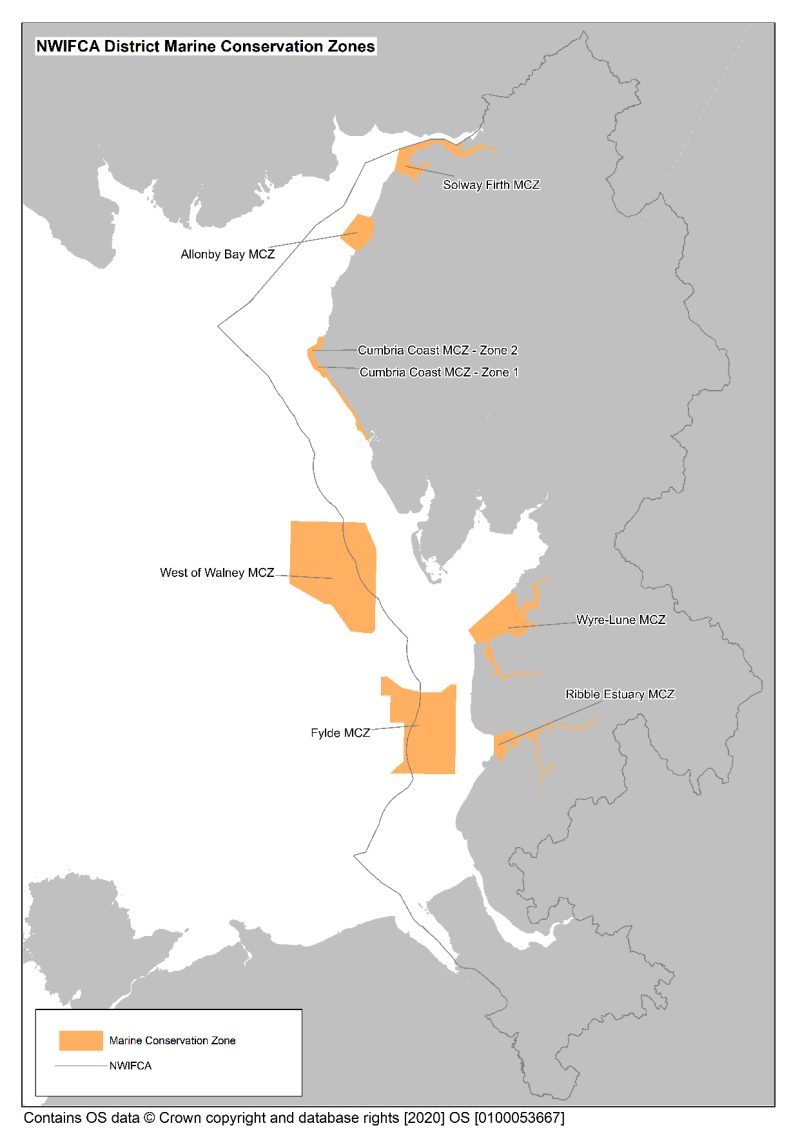
| Marine Conservation Zones |
| Allonby Bay MCZ |
| Cumbria Coast MCZ |
| Solway Firth MCZ |
| West Of Walney MCZ |
| Fylde MCZ |
| Ribble MCZ |
| Wyre Lune MCZ |
More information can be found below:
Link to interactive map showing IFCAs MPAs – IFCAs Management of Inshore Marine Protected Areas (association-ifca.org.uk)
Link to Marine Conservation Zone designations in England – Marine conservation zone designations in England – GOV.UK (www.gov.uk)